[Source: Reuters]
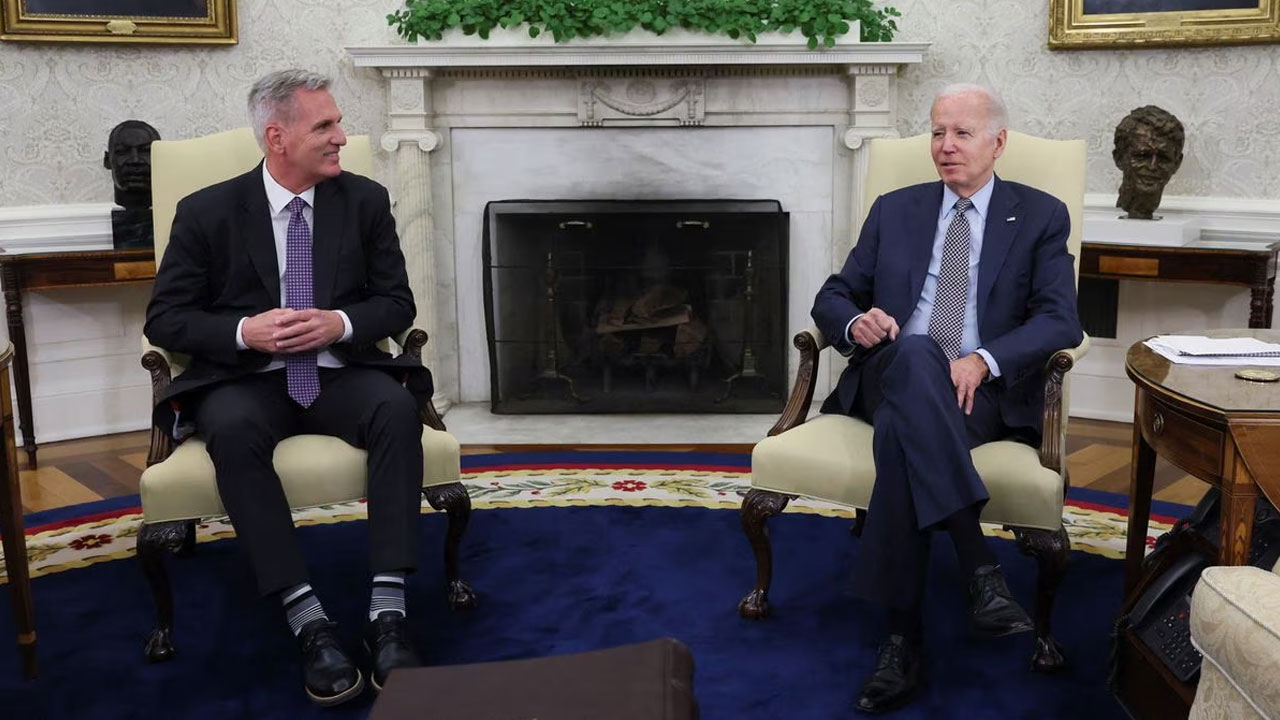
Negotiators for Democratic President Joe Biden and top congressional Republican Kevin McCarthy reconvened at the White House.
This is to try to close a deal to raise the United States’ $31.4 trillion debt ceiling and avoid a catastrophic default.
Time is running short, as the Treasury Department has warned that the federal government could be unable to pay all its bills by as soon as June 1 – just eight days away – and it will take several days to pass legislation through the narrowly divided Congress.
U.S. bond giant PIMCO said it believed negotiators needed to strike a deal by the middle of this week to make that deadline.
Biden and McCarthy, the speaker of the House of Representatives, remain deeply divided on how to move forward.
McCarthy told reporters on Wednesday that any deal must cut discretionary spending, not hold it steady as Biden has proposed, and not raise taxes.
He said he believed the two sides would reach a deal and avoid default.
Any deal that Biden and McCarthy reach will have a narrow path for passage through the divided Congress, where McCarthy’s Republicans hold a 222-213 House majority and Biden’s Democrats control the Senate by a 51-49 margin.
The compromises needed to win both chambers’ approval will also cost each party some votes from its most partisan members.
The months-long standoff has spooked Wall Street, weighing on U.S. stocks and pushing the nation’s cost of borrowing higher. U.S. stocks slid on Wednesday.
Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen on Wednesday said the United States will be unable to pay all its bills by early June, adding that it is difficult to be precise about the specific day the government will run out of resources.
That would trigger a Wall Street meltdown and push the U.S. economy toward recession, economists say. Medical providers that rely on government payments could be among the first to feel the heat.
Republicans want to cut discretionary spending for the 2024 fiscal year beginning in October by roughly 8%, while Democrats have pushed to hold it steady at this year’s rate.
Negotiators differ over Republicans’ proposals to impose new work requirements on benefits programs for low-income Americans and loosen energy permitting rules.
The White House has offered to limit discretionary spending for the coming two years, in line with previous bipartisan budget agreements. Republicans have offered spending caps for the coming six years.
Congress regularly needs to raise the nation’s self-imposed debt limit to cover the cost of spending and tax cuts it has already approved. It did so three times during Republican Donald Trump’s four years in the White House without triggering a similar standoff.
The last time the federal government came this close to default was in 2011, with a similar power divide in Washington – a Democratic president and Senate majority, and a Republican-controlled House.
Each party also faces opposition to the talks from within, with hardline Republicans insisting on the sharp spending cuts they passed in a House bill last month and progressive Democrats opposed to spending cuts or new work requirements.
Biden spent months saying he would not negotiate on raising the debt limit only to reverse course and begin talks with McCarthy in the last few weeks.
Stream the best of Fiji on VITI+. Anytime. Anywhere.

 Reuters
Reuters