[Source: Reuters]
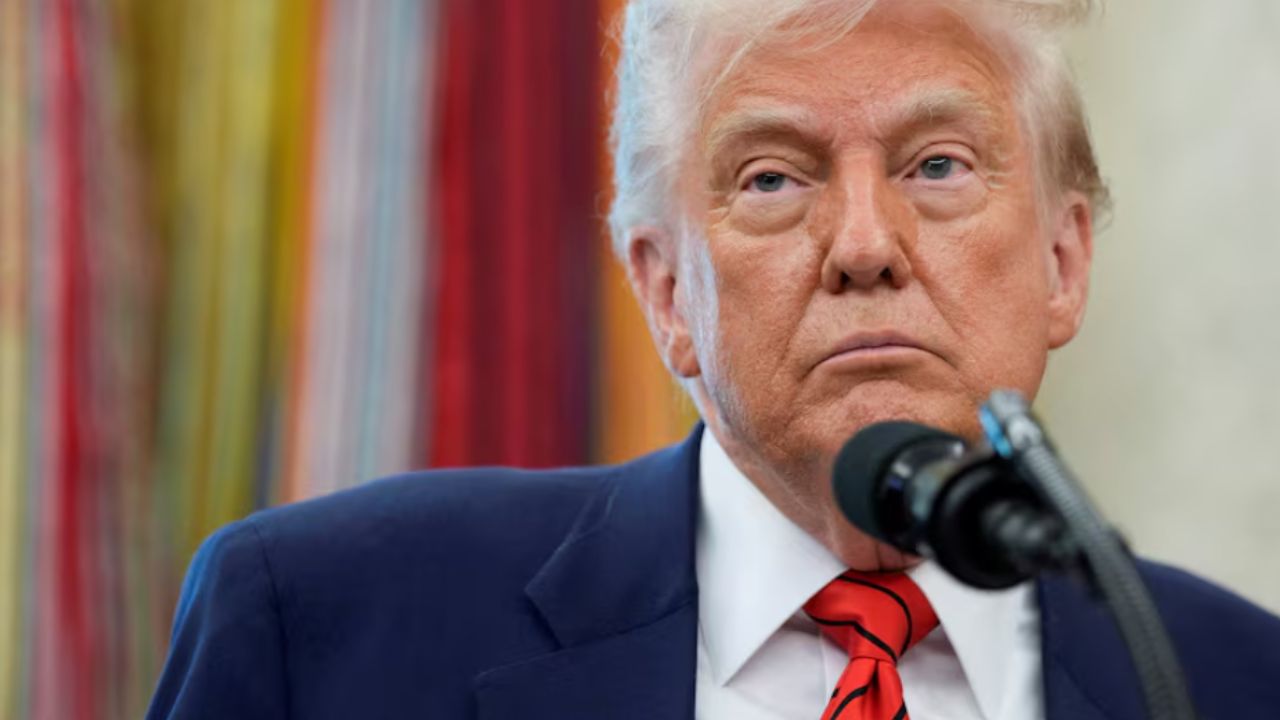
A U.S. sovereign downgrade by Moody’s has exacerbated investor worries about a looming debt time-bomb that could spur bond market vigilantes who want to see more fiscal restraint from Washington.
The ratings agency cut America’s pristine sovereign credit rating by one notch on Friday, the last of the major ratings agencies to downgrade the country, citing concerns about the nation’s growing $36 trillion debt pile.
The move came as Republicans who control the House of Representatives and the Senate seek to approve a sweeping package of tax cuts, spending hikes and safety-net reductions, which could add trillions to the U.S. debt pile. Uncertainty over the final shape of the so-called “Big Beautiful Bill” has investors on edge even as optimism has emerged over trade. The bill failed to clear a key hurdle on Friday even as U.S. President Donald Trump called for unity around the legislation.
The downgrade from Moody’s, which follows similar moves from Fitch in 2023 and Standard & Poor’s in 2011, will “eventually lead to higher borrowing costs for the public and private sector in the United States,” said Spencer Hakimian, founder of Tolou Capital Management in New York.
Even so, the ratings cut was unlikely to trigger forced selling from funds that can only invest in top-rated securities, said Gennadiy Goldberg, head of U.S. rates strategy at TD Securities, as most funds revised guidelines after the S&P downgrade. “But we expect it to refocus the market’s attention on fiscal policy and the bill currently being negotiated in Congress,” Goldberg said.
One question is how much pushback there will be in Congress over whether fiscal principles are being sacrificed, said Scott Clemons, chief investment strategist at Brown Brothers Harriman, adding that a bill that shows profligate spending could be a disincentive to add exposure to long-dated Treasuries.
The Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget, a nonpartisan think tank, estimates, opens new tab the bill could add roughly $3.3 trillion to the country’s debt by 2034 or around $5.2 trillion if policymakers extend temporary provisions.
Moody’s said on Friday successive administrations have failed to reverse the trend of higher fiscal deficits and interest costs, and it did not believe that material reductions in deficits will result from fiscal proposals under consideration.
Concern shows up in market pricing. A recent increase in the 10-year Treasury term premium – a measure of the return investors demand for the risk of holding long-dated debt – is partly a sign of underlying fiscal worry in the market, said Anthony Woodside, head of fixed income strategy at Legal & General Investment Management America. Woodside said the market was “not assigning much credibility” to the deficit being brought down in a material way.

Stream the best of Fiji on VITI+. Anytime. Anywhere.


 Reuters
Reuters