[Source: Reuters]
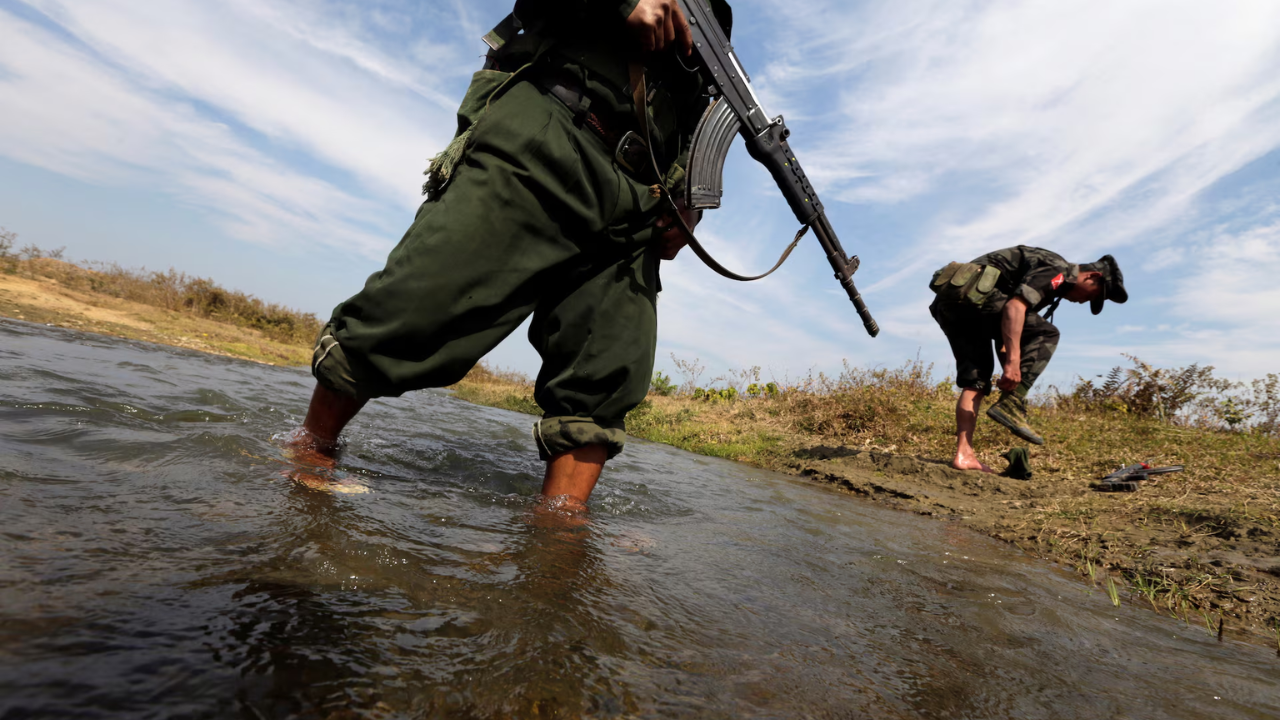
The global supply of heavy rare earths hinges in part on the outcome of a months-long battle between a rebel army and the Chinese-backed military junta in the hills of northern Myanmar.
The Kachin Independence Army since December has been battling the junta over the town of Bhamo, less than 100 km (62 miles) from the Chinese border, as part of the civil war that erupted after the military’s 2021 coup.
Nearly half the world’s supply of heavy rare earths is extracted from mines in Kachin state, including those north of Bhamo, a strategically-vital garrison town.
They are then shipped to China for processing into magnets that power electronic vehicles and wind turbines.
China, which has a near-monopoly over the processing of heavy rare earths, has threatened to halt buying the minerals mined in KIA-controlled territory unless the militia stops trying to seize full control of Bhamo, according to three people familiar with the matter.
The ultimatum issued by Chinese officials to the KIA in a meeting earlier this year, which is reported by Reuters for the first time, underscores how Beijing is wielding its control of the minerals to further its geopolitical aims.
One of the people, a KIA official, said the Chinese demand was made in May, without detailing where the discussions took place. Another person, a KIA commander, said Beijing was represented by foreign ministry officials at the talks.
Reuters could not determine whether China had carried out its threat.
Fighting in the region has restricted mining operations and rare-earth exports from Myanmar have plunged this year.
China spooked global supply chains this spring when it restricted exports of the minerals in retaliation against U.S. President Donald Trump’s tariffs. It is now using its dominance to shore up
Myanmar’s beleaguered junta, which China sees as a guarantor of its economic interests in its backyard.
China’s foreign ministry said in response to Reuters’ questions that it was not aware of the specifics of deliberations with the KIA.
“An early ceasefire and peace talks between the Myanmar military and the Kachin Independence Army are in the common interests of China and Myanmar as well as their people,” a ministry spokesperson said.
A senior KIA general did not respond to a request for comment.
The KIA official, who spoke on condition of anonymity to discuss sensitive matters, said Beijing also offered a carrot: greater cross-border trade with KIA-controlled territories if the militia abandoned efforts to seize Bhamo, a logistics hub for the junta that’s home to some 166,000 people.
“And if we did not accept, they would block exports from Kachin State, including rare-earth minerals,” said the official, who did not elaborate on the consequences of an economic blockade.
Beijing is not seeking to resolve the wider civil war but it wants fighting to subside in order to advance its economic interests, said David Mathieson, an independent Myanmar-focused analyst.
Stream the best of Fiji on VITI+. Anytime. Anywhere.


 Reuters
Reuters